Let Us Be Your Guide Through The Mortgage Process.
When you work with us, we’ll pair you with an experienced agent to take you step-by-step through the mortgage process. You’ll receive personalized, one-on-one service designed to get you across the finish line.
Notable Terms.
Mortgage Term: The length of time that you’re locked into your rate and conditions.
Down Payment: Any down payment less than 20% requires mortgage default insurance. Over 20% is considered a conventional mortgage, which doesn’t require insurance.
Mortgage Type: An open mortgage allows the borrower the option to pay off all or any of the balance owing on the mortgage at any time, without a penalty but tends to come with a higher interest rate.
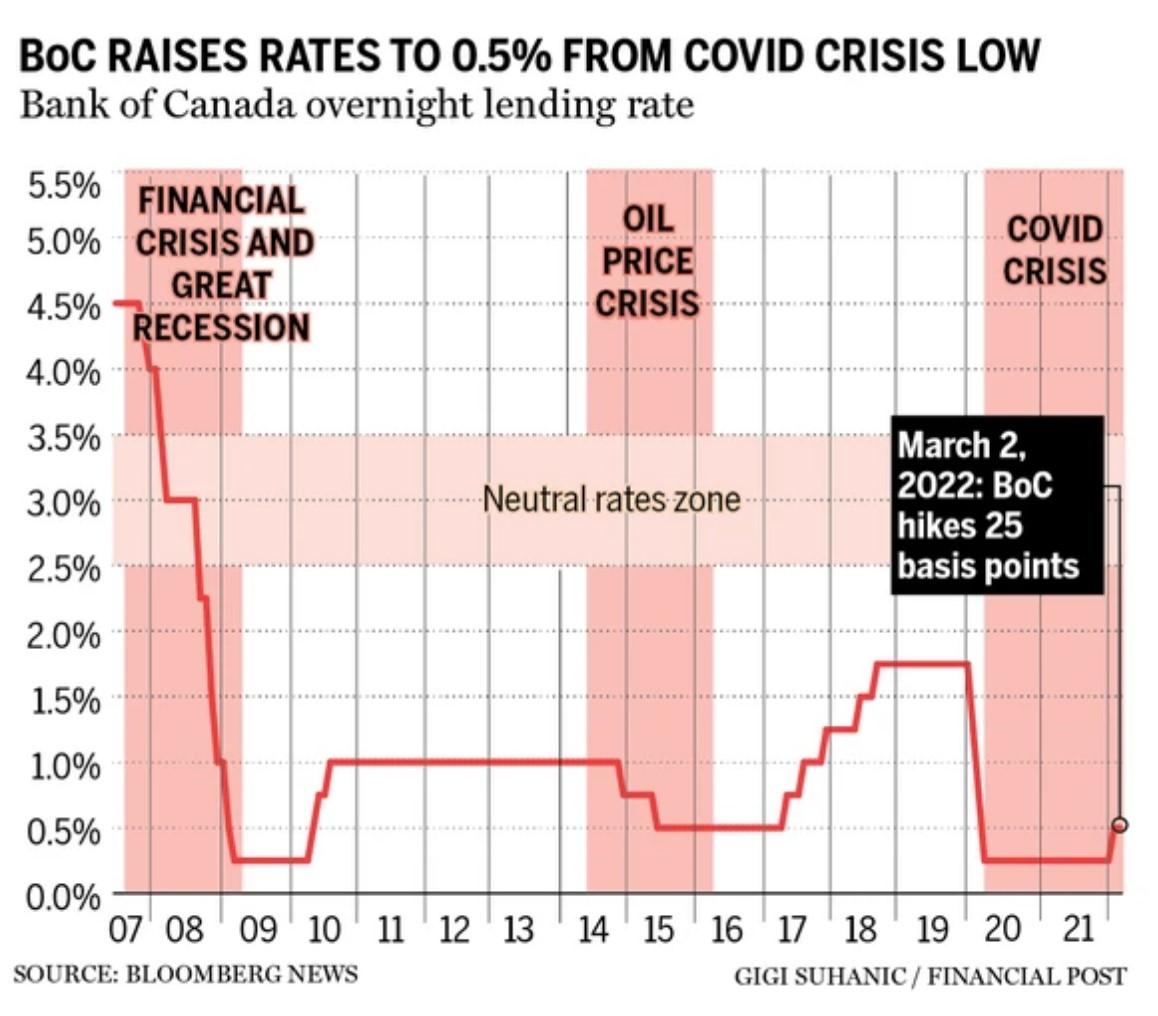
Mortgage Rate: You’ll choose either a fixed or variable rate mortgage. Variable rates are often lower but involve more risk, as your payments may fluctuate with the rate set by the Bank of Canada. Fixed rates mean you are locked in for a term and your monthly mortgage payment is set in advance.
Amortization: The number of years it takes to repay your entire mortgage loan amount, based on a fixed payment schedule. Most lenders offer 25-year amortizations.
Closing Costs: Don’t forget about closing costs. Lenders typically like to see that you have at least 1.5% of the purchase price to cover these costs.
Mortgage Stress-Test: Federal regulations have made qualifying for a mortgage a little tougher. Regardless of the low rates offered, you’ll need to qualify to ensure that if mortgage interest rates go up, you’ll still be able to afford your payments.
Looking for your First Mortgage? There are Programs and Rebates to Help.
THE HOME BUYERS’ PLAN (HBP)
If you’re a first-time homebuyer, the HBP allows you to withdraw up to $35,000 from your RRSPs tax-free to put toward buying your first home. The HBP allows you to pay back the withdrawn funds within a 15-year period.
THE FIRST-TIME HOME BUYER INCENTIVE
The First-Time Home Buyer Incentive helps people across Canada purchase their first home. The program offers 5% or 10% of the home’s purchase price to put toward a down payment. You pay back the same percentage of the value of your home when you sell it or within a 25-year window.
The Mortgage Financing Process.
The number one question for someone new to the mortgage process is “what does this process entail?”. The following is a simple outline to give you an idea of the process and help you understand what to expect as you embark on your home buying journey!
STEP 1 – BE PREPARED
Having the following information on hand before meeting with your mortgage professional will help them determine what you qualify for and help them determine the best mortgage product for you:
Contact information for your employer and your employment history
Proof of address and your address history
Government-issued photo ID with your current address
Proof of income for your mortgage application
Down payment proof (amount and source)
Savings and investments proof
Details of current debts and other financial obligations
STEP 2 – GET PRE-APPROVED
One of the best things any potential homeowner can do when starting the home buying process is to get pre-approved. Mortgage pre-approval requires submission and verification of your financial history and can help you determine your price range, understand the monthly mortgage payment associated with that price range and provide the mortgage rate for your first term.
It is important to note that pre-approval does not mean that a lender has fully reviewed your documentation and you may still need the approval of a mortgage insurer. However, it does have a lot of benefits that can give you a “leg-up” in your search!
BENEFITS OF PRE-APPROVAL
Getting pre-approved not only makes the search easier by helping to determine your price range and budget, but pre-approval also guarantees the interest rate for 90-120 days while you search for that perfect home. Plus, the rate will automatically be adjusted down with any market reductions. Another benefit to pre-approval is that, when it comes time to purchase, pre-approval lets the seller know that securing financing should not be an issue. This is extremely beneficial in competitive markets where lots of offers may be coming in.
Quick Tip: Being entirely candid with your home-buying team throughout the process will be vital! Hidden debt or buying a big-ticket item during your 90-120 day pre-approval can change the amount you are able to borrow. It is best to refrain from any major purchases (such as a new car) or life changes (such as changing jobs) until after closing and you have the keys to your new home!
STEP 3 – HIRE A REALTOR
In today’s competitive real estate market, it can be very difficult to acquire property WITHOUT the help of a realtor. One of the reasons realtors are integral to the home buying process is that they can provide access to properties that never even make it to the MLS website. Realtors also gain access to information about homes that may come onto the market before a listing is even signed.
Most importantly though, a realtor understands the ins-and-outs of the home buying process and can tell you how to be successful in your endeavors to purchase a home by guiding you through the process from the first viewing to having your bid accepted.
STEP 4 – SHOP THE MARKET & MAKE AN OFFER
Once you have found the property that meets your needs, you’ll put in an offer that’ll be accepted or countered. This may go back and forth until you reach an acceptable price with the vendor.
STEP 5 – OFFER IS ACCEPTED
Once your offer is accepted with the condition of financing, you will need to do a few things to finalize the sale:
Ask for a realtor intro between your mortgage professional and realtor.
An appraisal may be required, which will be determined and arranged by your mortgage professional.
Send in any remaining documents required for financing (income confirmation, down payment confirmation, etc).
Arrange a home inspection.
Receive the lender’s approval on property and final approval letter.
STEP 6 – REMOVE CONDITIONS
At this point, your financing is in place and you’re ready to proceed with the purchase of the property.
STEP 7 – LAWYER’S OFFICE
You’ll be asked to provide any money that’s to be used as your down payment, which is not already on deposit with your realtor. Typically, you’ll go in 1-2 days prior to the completion date.
DLC-FCF