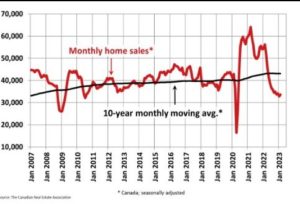
The Canadian Real Estate Association says home sales in February bounced 2.3% from the previous month. Homeowners and buyers were comforted by the guidance from the Bank of Canada that it would likely pause rate hikes for the first time in a year.
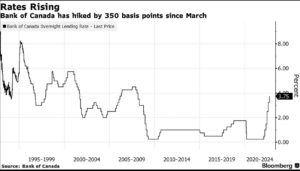
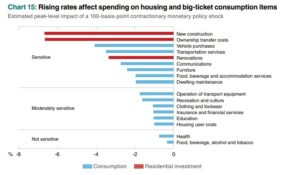
The Canadian aggregate benchmark home price dropped 1.1% in February, the smallest month-to-month decline of rapid interest rate increases in the past year. The unprecedented surge in the overnight policy rate, from a mere 25 bps to 450 bps, has not only slowed housing–the most interest-sensitive of all spending–but has now destabilized global financial markets.
In the past week, three significant US regional financial institutions have failed, causing the Fed, the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation and the Treasury to take dramatic action to assure customers that all money in both insured and uninsured deposits would be refunded and the Fed would provide a financial backstop to all financial institutions.
Stocks plunged on Monday as the flight to the safe haven of Treasuries and other government bonds drove shorter-term interest rates down by unprecedented amounts. With the US government’s reassurance that the failures would be ring-fenced, markets moderately reversed some of Monday’s movements.
But today, another bogeyman, Credit Suisse, rocked markets again, taking bank stocks and interest rates down even further. All it took was a few stern words from Credit Suisse Group AG’s biggest shareholder on Wednesday to spark a selloff that spread like wildfire across global markets.
Credit Suisse’s shares plummeted 24% in the biggest one-day selloff on record. Its bonds fell to levels that signal deep financial distress, with securities due in 2026 dropping 20 cents to 67.5 cents on the dollar in New York. That puts their yield over 20 percentage points above US Treasuries.
For global investors still, on edge after the rapid-fire collapse of three regional US banks, the growing Credit Suisse crisis provided a new reason to sell risky assets and pile into the safety of government bonds. This kind of volatility unearths all the investors’ and institutions’ missteps. Panic selling is never a good thing, and traders are scrambling to safety, which means government bond yields plunge, gold prices surge, and households typically freeze all discretionary spending and significant investments. This, alone, can trigger a recession, even when labour markets are exceptionally tight and job vacancies are unusually high.
Canadian bank stocks have been sideswiped despite their much tighter regulatory supervision. Fears of contagion and recession persist. Job #1 for the central banks is to calm markets, putting inflation fighting on the back burner until fears have ceased.
Larry Fink, CEO of Blackrock, reminded us yesterday that previous cycles of rapid interest rate tightening “led to spectacular financial flameouts” like the bankruptcy of Orange County, Calif., in 1994, he wrote, and the savings and loan crisis of the 1980s and ’90s. “We don’t know yet whether the consequences of easy money and regulatory changes will cascade throughout the US regional banking sector (akin to the S.&L. crisis) with more seizures and shutdowns coming,” he said.
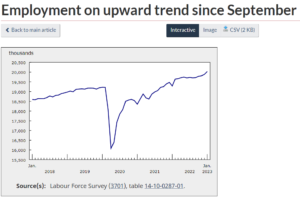
So it is against that backdrop that we discuss Canadian housing. The past year’s surge in borrowing costs triggered one of the record’s fastest declines in Canadian home prices. Sales were up in February, the markets tightened, and the month-over-month price decline slowed.
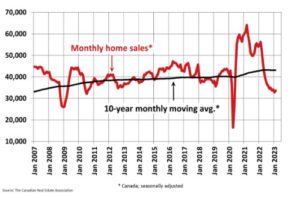
New Listings
The number of newly listed homes dropped 7.9% month-over-month in February, led by double-digit declines in several large markets, particularly in Ontario.
With new listings falling considerably and sales increasing in February, the sales-to-new listings ratio jumped to 58.4%, the tightest since last April. The long-term average for this measure is 55.1%.
There were 4.1 months of inventory on a national basis at the end of February 2023, down from 4.2 months at the end of January. It was the first time the measure had shown any sign of tightening since the fall of 2021. It’s also a whole month below its long-term average.
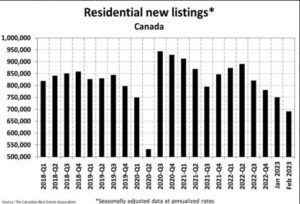
Home Prices
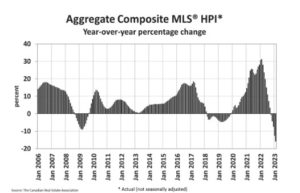
The Aggregate Composite MLS® Home Price Index (HPI) was down 1.1% month-over-month in February 2023, only about half the decline recorded the month before and the smallest month-over-month drop since last March.
The Aggregate Composite MLS® HPI sits 15.8% below its peak in February 2022.
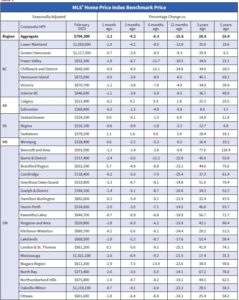
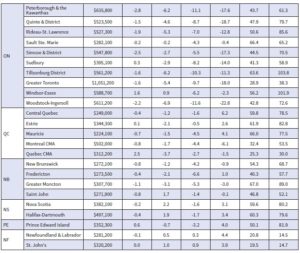
Looking across the country, prices are down from peak levels by more than they are nationally in most parts of Ontario and a few parts of British Columbia and down by less elsewhere. While prices have softened to some degree almost everywhere, Calgary, Regina, Saskatoon, and St. John’s stand out as markets where home prices are barely off their peaks. Prices began to stabilize last fall in the Maritimes. Some markets in Ontario seem to be doing the same now.
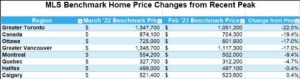
The table below shows the decline in MLS-HPI benchmark home prices in Canada and selected cities since prices peaked a year ago when the Bank of Canada began hiking interest rates. More details follow in the second table below. The most significant price dips are in the GTA, Ottawa, and the GVA, where the price gains were spectacular during the Covid-shutdown.
Despite these significant declines, prices remain roughly 28% above pre-pandemic levels.
Bottom Line
Last month I wrote, “The Bank of Canada has promised to pause rate hikes assuming inflation continues to abate. We will not see any action in March. But the road to 2% inflation will be a bumpy one. I see no likelihood of rate cuts this year, and we might see further rate increases. Markets are pricing in additional tightening moves by the Fed.
There is no guarantee that interest rates in Canada have peaked. We will be closely monitoring the labour market and consumer spending.”
Given the past week’s events, all bets are off regarding central bank policy until and unless market volatility abates and fears of a global financial crisis diminish dramatically. Although the overnight policy rates have not changed, market-driven interest rates have fallen precipitously, which implies the markets fear recession and uncontrolled mayhem. As I said earlier, job #1 for the Fed and other central banks now is to calm these fears. Until that happens, inflation-fighting is not even a close second. I hope it happens soon because what is happening now is not good for anyone.
Judging from experience, this could ultimately be a monumental buying opportunity for the stocks of all the well-managed financial institutions out there. But beware, markets are impossible to time, and being too early can be as painful as missing out.
Dr. Sherry Cooper
Chief Economist, Dominion Lending Centres
drsherrycooper@dominionlending.ca